[Spring JPA #5] 엔티티 상태와 Cascade
- 📚 Spring/Spring JPA
- 2020. 7. 14. 10:04
| 엔티티 상태
JPA에서는 엔티티의 상태를 다음과 같이 나눈 후 사용자가 요청한 사항에 맞추어 관리하게 됩니다.
Transient : JPA가 엔티티를 나타내는 객체에 대한 정보를 모르는 상태
Persistent : JPA가 엔티티를 관리 중인 상태 (1차 캐시, Dirty Checking, Write Behind, ..)
- Dirty Checking : 객체의 변경사항을 계속 감지
- Write Behind : 객체의상태변화을 데이터베이스에 최대한 늦게, 필요한 시점에 반영한다는것이다.
Detached : JPA가 더이상 엔티티를 관리하지 않는 상태
Removed : JPA가 엔티티를 관리하는 상태에서 이 엔티티를 삭제하기로한 상태
- save를 했다고 바로 DB에 쿼리를 날리는 것은 아니다.
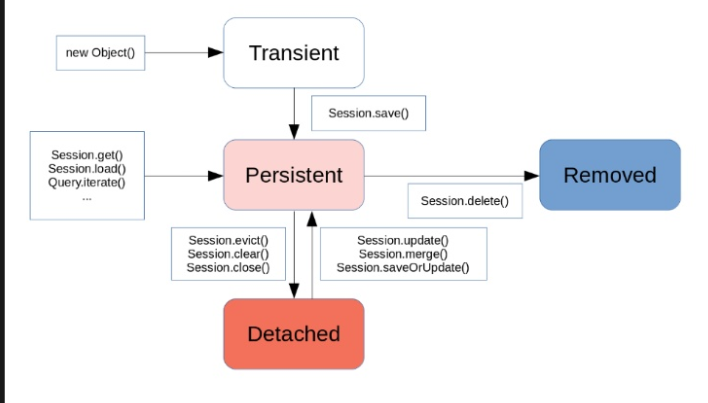
- Casade 옵션 : child에 있는 연관관계의 객체도 같이 persistent 상태가 되어 저장이 된다.
| CASCADE 옵션이 없을 경우
소스코드
package com.kyhslam;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.OneToMany;
@Entity
public class Post {
@Id @GeneratedValue
private Long id;
private String title;
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "post")
private Set<Comment> comments = new HashSet<>();
public void addComment(Comment comment) {
this.getComments().add(comment);
comment.setPost(this);
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public Set<Comment> getComments() {
return comments;
}
public void setComments(Set<Comment> comments) {
this.comments = comments;
}
}
package com.kyhslam;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.ManyToOne;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
public class Reply {
@Id @GeneratedValue
private Long id;
private String content;
@ManyToOne
private Post post;
public Post getPost() {
return post;
}
public void setPost(Post post) {
this.post = post;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
}
- 엔티티는 양방향 매핑이 되어 있는 상태이다.
- Casecade옵션을 주지 않은 상태이기 때문에 아래의 ApplicationRunner를 실행시켜도 Post에 대한 정보만 DB에 저장이 되고 Reply는 반영되지 않는다.
package com.kyhslam;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import javax.persistence.PersistenceContext;
import javax.transaction.Transactional;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationArguments;
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationRunner;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Transactional
public class JpaRunner implements ApplicationRunner {
@PersistenceContext
EntityManager entityManager;
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
Post post = new Post();
post.setTitle("Spring data Jpa");
Reply reply = new Reply();
reply.setContent("Seeing jpa");
post.addReply(reply);
Reply reply3 = new Reply();
reply3.setContent("Seeing jpa22");
post.addReply(reply3);
Session session = entityManager.unwrap(Session.class);
session.save(post);
}
}
결과
| CASCADE 옵션을 적용했을 경우
- Post 엔티티에 cascade = CascadeType.ALL 옵션을 적용하였다.
@Entity
public class Post {
@Id @GeneratedValue
private Long bno;
private String title;
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "post", cascade = CascadeType.ALL)
private Set<Reply> replys = new HashSet<>();
public void addReply(Reply reply) {
this.getReplys().add(reply);
reply.setPost(this);
}
public Long getBno() {
return bno;
}
public void setBno(Long bno) {
this.bno = bno;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public Set<Reply> getReplys() {
return replys;
}
public void setReplys(Set<Reply> replys) {
this.replys = replys;
}
}
결과
SELECT * FROM post;
BNO|TITLE |
---|---------------|
1|Spring data Jpa|
SELECT * FROM reply;
ID|CONTENT |POST_BNO|
--|------------|--------|
2|Seeing jpa | 1|
3|Seeing jpa22| 1|'📚 Spring > Spring JPA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Spring JPA #7] Query (0) | 2020.07.15 |
|---|---|
| [Spring JPA #6] Fetch (0) | 2020.07.15 |
| [Spring JPA #4] 관계 맵핑 (0) | 2020.06.28 |
| [Spring JPA #3] Entity 매핑 및 Value 타입 (0) | 2020.06.27 |
| [Spring JPA #2] JPA 엔티티 매핑 용어 정리 (0) | 2020.06.27 |